

If a variable y is a linear (y = a + bx) transformation of x then the variance of y is b² times the variance of x and the standard deviation of y is b times the variance of x. When distributions are approximately normal, SD is a better measure of spread because it is less susceptible to sampling fluctuation than (semi-)interquartile range. is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to. For any symmetrical (not skewed) distribution, half of its values will lie one semi-interquartile range either side of the median, i.e. Semi-interquartile range is half of the difference between the 25th and 75th centiles.
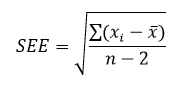
Interquartile range is the difference between the 25th and 75th centiles. This is not the case when there are extreme values in a distribution or when the distribution is skewed, in these situations interquartile range or semi-interquartile are preferred measures of spread. SD is the best measure of spread of an approximately normal distribution. All three terms mean the extent to which values in a distribution differ from one another.
How to calculate standard error from standard deviation how to#
This will show how to calculate the standard deviation of a set of data. The spread of a distribution is also referred to as dispersion and variability. Standard deviation is a measurement of how spread out the numbers are of a set of data. It is an empirical estimate of the SE of the sample sum. For each box, this standard deviation will tend to stabilize after a few thousand samples. The unbiased estimate of population variance calculated from a sample is: Experiment using by drawing a large number of samples from different boxes pay attention to 'SD(samples),' which gives the standard deviation of the observed values of the sample sum, each of which is the sum of n draws. Variance is usually estimated from a sample drawn from a population. SD is calculated as the square root of the variance (the average squared deviation from the mean). The standard deviation of the mean (SD) is the most commonly used measure of the spread of values in a distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
